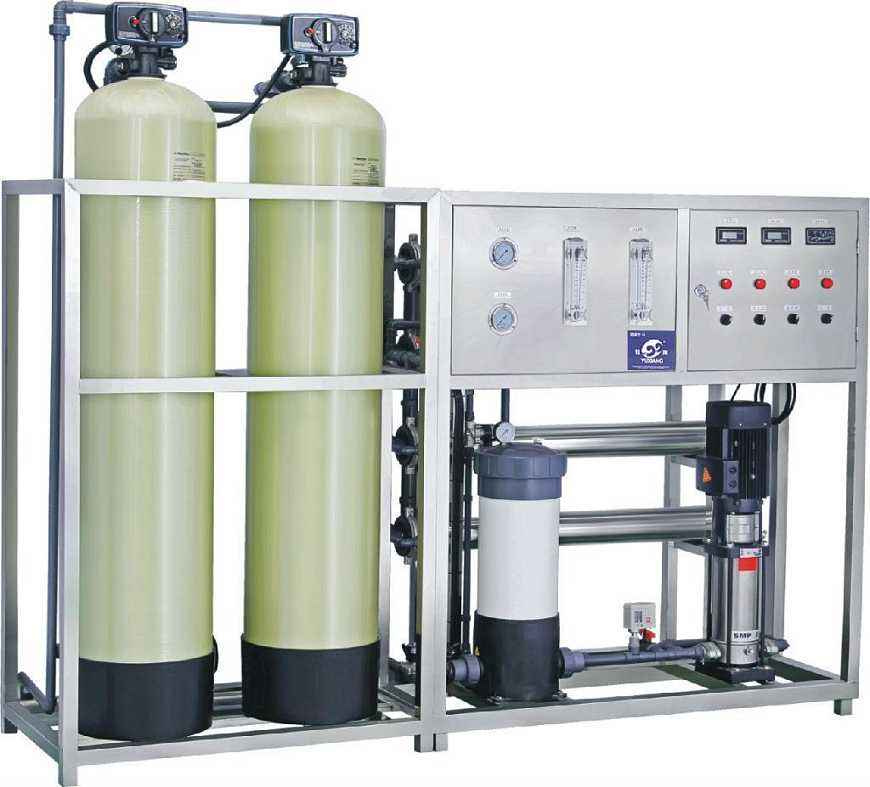

Reverse Osmosis Equipment
Reverse osmosis is a new membrane separation technology that relies on a reverse osmosis membrane to separate the solvent from the solute in a solution under pressure, achieving the purpose of purified water and concentration.
Application Range: Electronics, pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals, beverages, brewing, dairy products, civil and other industries for water use.
Equipment Features: High desalination rate, stable operation, higher water quality assurance, low operating costs, no need for chemical regeneration, and continuous operation.
Reverse Osmosis Equipment Technical Parameters:
Inlet water temperature requirement: 1-45℃, PH: 3-10
Sludge Index: SDI < 5, Turbidity NTU < 1, Residual Chlorine < 0.1ppm, Removal Rate > 97%
Power Supply: 380V/50HZ - 220V/50HZ
1. Pretreatment of Reverse Osmosis Equipment
Composed of multi-media filter, activated carbon filter, and fully automatic water softener.
Multi-media Filter: Consisting of a fully automatic control valve, glass steel tank, and quartz sand with different grading ratios. It can effectively remove suspended solids and some colloidal substances from the raw water, reducing the turbidity of the raw water. It can also automatically perform backwashing.
Activated Carbon Filter: Consisting of a fully automatic control valve, high-quality glass tank, and different water purification grades of activated carbon. It can effectively adsorb harmful substances such as heavy metals, free chlorine, chloroform, etc., from the raw water. It can also automatically perform backwashing.
Food Grade Water Softener: Consisting of a fully automatic control valve, high-quality glass steel tank, and food grade resin. Through the food-grade water softener, calcium and magnesium ions in the water can be effectively removed. This ensures that the reverse osmosis membrane will not be affected by scaling during operation, extending its lifespan. It can also automatically regenerate itself.
2. Main Part of Reverse Osmosis Equipment
The main part of the reverse osmosis equipment mainly consists of a security filter, high-pressure pump, reverse osmosis membrane, and various control and display instruments.
Security Filter: The security filter is the final protection before the raw water enters the membrane. It can effectively remove substances larger than 5μm that may leak from the pretreatment process. Its main function is to prevent suspended particles from entering the reverse osmosis membrane elements and depositing on the membrane surface, thus contaminating the membrane elements.
High-pressure Pump: Provides the necessary pressure for reverse osmosis, ensuring the separation of the solvent and solute. The high-pressure pump is one of the key components of the reverse osmosis equipment.
Reverse Osmosis Membrane Module: The reverse osmosis membrane module is composed of polymeric fibers with a highly ordered matrix structure. Its pore size ranges from 1-10 angstroms, which is equivalent to one-hundred-billionth to one-billionth of a meter (equivalent to one-sixth of the size of Escherichia coli and one-third of the size of a virus). Utilizing the separation characteristics of the reverse osmosis membrane, it can effectively remove dissolved salts, colloids, organic matter, heavy metals, trihalomethanes intermediates generated by chlorination, bacteria, and microorganisms from the solvent.
Reverse Osmosis Membrane Shell: Used to accommodate the reverse osmosis membrane elements, withstand pressure, and create a high-pressure environment for reverse osmosis operations.
Flowmeter: The pure water flowmeter and the concentrated water flowmeter measure the instantaneous flow of RO pure water and concentrated water, respectively.
Pressure Gauge: Measures the water pressure at various points of the reverse osmosis equipment.
Concentrated Water Regulating Valve: Used to adjust the operating pressure of the RO equipment, the ratio of pure water to concentrated water, and the production of pure water.
Conductivity Meter: Monitors the conductivity of the reverse osmosis effluent.
Low-pressure Switch: Prevents the RO high-pressure pump from running idle or operating beyond the limit low pressure.
Liquid Level Controller: Automatically stops or starts the reverse osmosis equipment based on the liquid level of the raw water tank and the pure water tank.
Electrical Control System: Consisting of instrumentation such as conductivity meters, control equipment, and serving as the control center for the reverse osmosis equipment.
The use of reverse osmosis equipment to produce pure water and ultra-pure water requires comprehensive design based on each user's industry characteristics, equipment water production requirements, on-site conditions, and other factors.
III. System Flow Chart of Reverse Osmosis Equipment (Parameters are for reference only, actual products prevail):
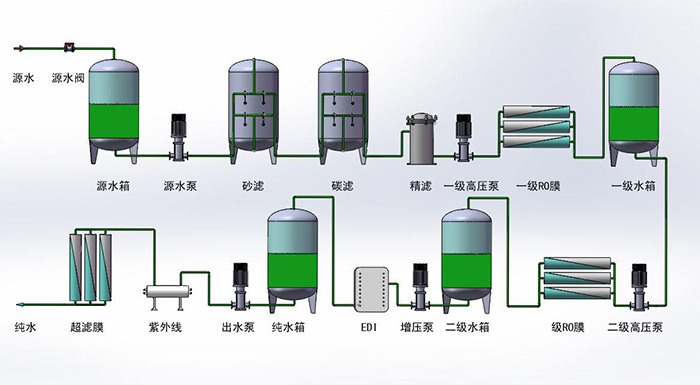
IV. Specification and Technical Parameters of Reverse Osmosis Equipment (Parameters are for reference only, and the actual product shall prevail):
Model | water yield (m3/h) | Motor power (kw) | Inlet pipe diameter (inch) | Outside diameter size (mm) | Transport weight (kg) |
JMRO-0.5 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 3/4" | 500×664×1550 | 140 |
JMRO-1 | 1 | 2.2 | 1" | 1600×664×1550 | 250 |
JMRO-2 | 2 | 4.0 | 1.5" | 2500×700×1550 | 360 |
JMRO-3 | 3 | 4.0 | 1.5" | 3300×700×1820 | 560 |
JMRO-5 | 5 | 8.5 | 2" | 3300×700×1820 | 600 |
JMRO-8 | 8 | 10.0 | 2" | 3600×875×2000 | 750 |
JMRO-10 | 10 | 11.0 | 2" | 3600×875×2000 | 800 |
JMRO-15 | 15 | 16.0 | 2.5" | 4200×1250×2000 | 840 |
JMRO-20 | 20 | 22.0 | 3" | 6600×2200×2000 | 1540 |
JMRO-30 | 30 | 37.0 | 4" | 6600×1800×2000 | 2210 |
JMRO-40 | 40 | 45.0 | 5" | 6600×1625×2000 | 2370 |
JMRO-50 | 50 | 55.0 | 6" | 6600×1625×2000 | 3500 |
JMRO-60 | 60 | 75.0 | 6" | 6600×1000×2000 | 3950 |
JMRO-80 | 80 | 90.0 | 8" | 6600×1000×2000 | 4500 |
HLRO-100 | 100 | 110.0 | 10" | 6600×1250×2000 | 5700 |
V. Fields and Application Industries of Reverse Osmosis Equipment:
(1) Electric Power Industry: boiler feed water, cooling water, deoxygenated water, desalted water, boiler water softening, etc.;
(2) Electronic Industry: ultrapure water for semiconductor industry, cleaning water for integrated circuits, formula water, metallurgy, copper industry, optics, integrated circuits, silicon wafers, flushing of electronic components such as display tubes, boiler feed water for power and thermal power industries;
(3) Food Industry: formula water, production water, drinking purified water, beverages, beer, liquor and other water uses, desalination of sea water and brackish water, etc.;
(4) Pharmaceutical Industry: process water, preparation water, washing water, injection water, infusion, injections, tablets, biological products, sterile water equipment;
(5) Beverage Industry: formula water, production water, washing water;
(6) Chemical Industry: production water, waste water treatment;
(7) Drinking Water Projects: ultrapure water preparation, purification of domestic drinking water;
(8) Petrochemical Industry: oilfield injection water, circulating water, petrochemical waste water, deep treatment of sewage;
(9) Sea Water Desalination: production and domestic water use in island areas, water-scarce coastal areas, ships, and offshore oilfields;
(10) Environmental Protection Field: recovery of precious metals from electroplating rinse water, water recycling, achieving zero or micro-emissions.
VI. Common Problems and Solutions of Reverse Osmosis Equipment:
Reverse osmosis equipment may encounter various problems during use. The following are some common problems, their possible causes, and handling measures:
1. Equipment Does Not Start:
* Cause: Electrical wiring faults, thermal protection elements not reset after protection, under-pressure in the water circuit, etc.
* Handling Measures: Check insurance and wiring, reset thermal protection elements, ensure water supply pressure, check water level switches.
2. Inlet Electromagnetic Valve Not Open:
* Cause: Disconnected wiring, internal fault of the solenoid valve, damaged solenoid valve coil, etc.
* Handling Measures: Check wiring, disassemble the solenoid valve for repair or replacement of parts and coils.
3. Pump Runs But Does Not ReachRated Pressure and Flow:
* Cause: Pump running in reverse, dirty security filter cartridge, air in the pump, rinse solenoid valve not open, etc.
* Handling Measures: Rewire, clean or replace the filter cartridge, remove air from the pump, adjust pressure.
4. System Pressure Increases and Pump Noise Is Loud:
* Cause: Insufficient raw water flow, unstable raw water flow with vortex, etc.
* Handling Measures: Check the raw water pump and piping, check for leaks in the piping.
5. Electromagnetic Valve Does Not Close After Rinsing:
* Cause: Faulty solenoid valve control components and wiring, mechanical fault of the solenoid valve, etc.
* Handling Measures: Check and replace solenoid valve control components and wiring, repair or replace the solenoid valve.
In addition, reverse osmosis equipment may also face the following problems:
* High feed water pressure: may be due to improper adjustment of the high-pressure pump outlet valve, blocked piping, problems with the concentrated water control valve, or too low recovery rate.
* High recovery rate: may be due to excessively high feed water pressure or insufficient feed water flow rate.
* High pressure drop across the reverse osmosis equipment: may be due to high concentrated water flow rate or membrane element fouling.
* High-pressure pump stops running: may be due to excessively high pump outlet pressure or excessively low pump inlet water pressure.
* Water production decreases: may be due to low feed water temperature, low feed water pressure, high concentrated water concentration, or membrane fouling.
* Water production increases: may be due to high feed water pressure or high feed water temperature.
* Both product water conductivity and concentrated water conductivity increase: may be due to blockage of the concentrated water piping or concentrated water control valve, or excessively high recovery rate.
These problems require investigation and handling based on specific situations. During operation, it is important to ensure safety, follow equipment operation manuals, and comply with relevant safety regulations. If the problem is complex or cannot be solved independently, it is recommended to contact professional maintenance personnel or equipment manufacturers for further handling.

